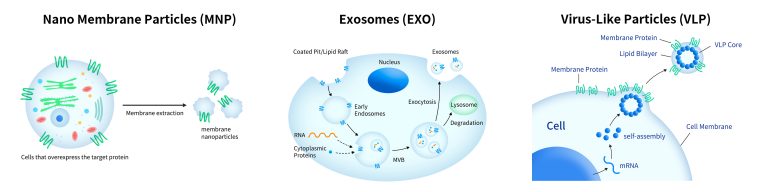
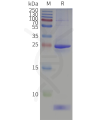
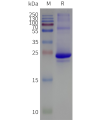
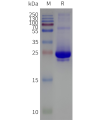
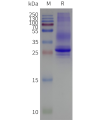
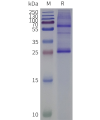
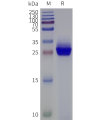
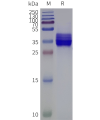
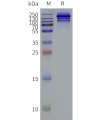
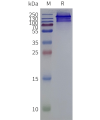
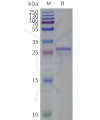
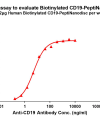
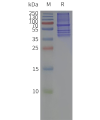
- Detergent Solubilization of Membrane Proteins
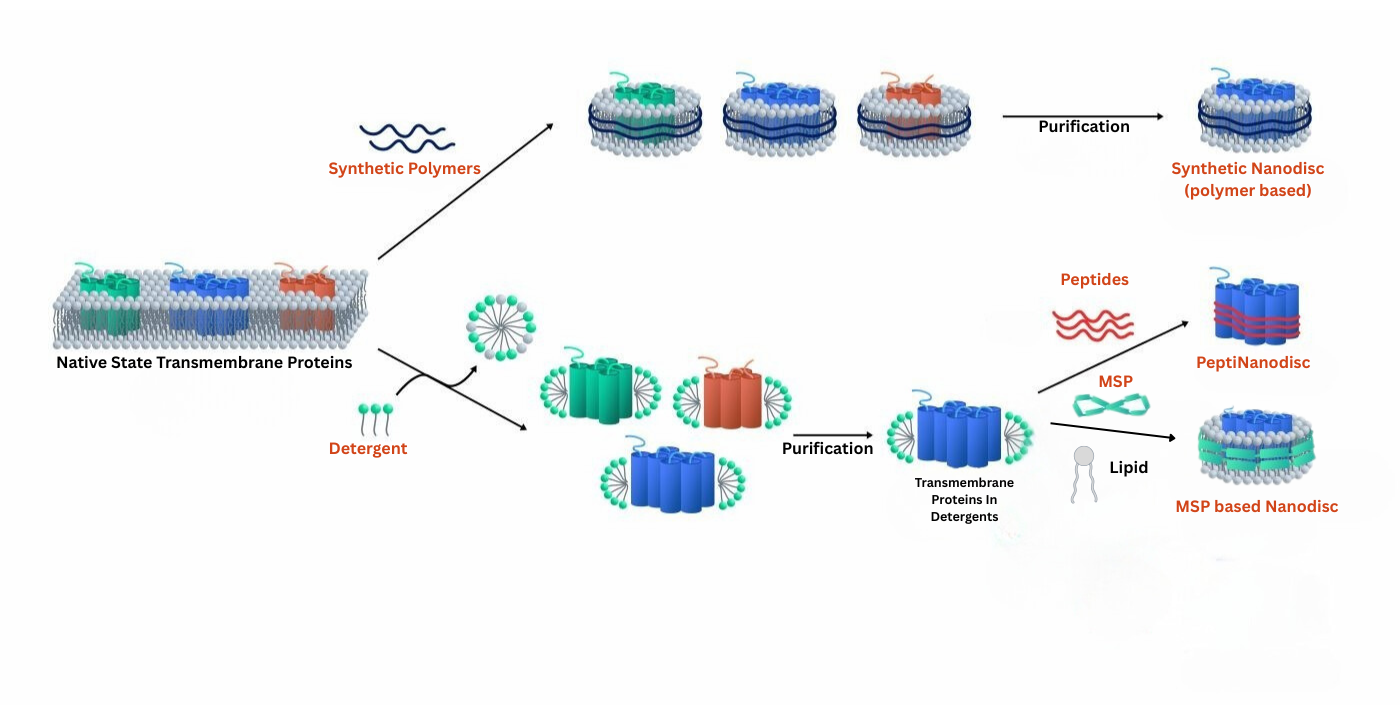
Detergents are amphipathic molecules that form micelles above a critical concentration, enabling solubilization of active membrane proteins as stable protein–detergent complexes.
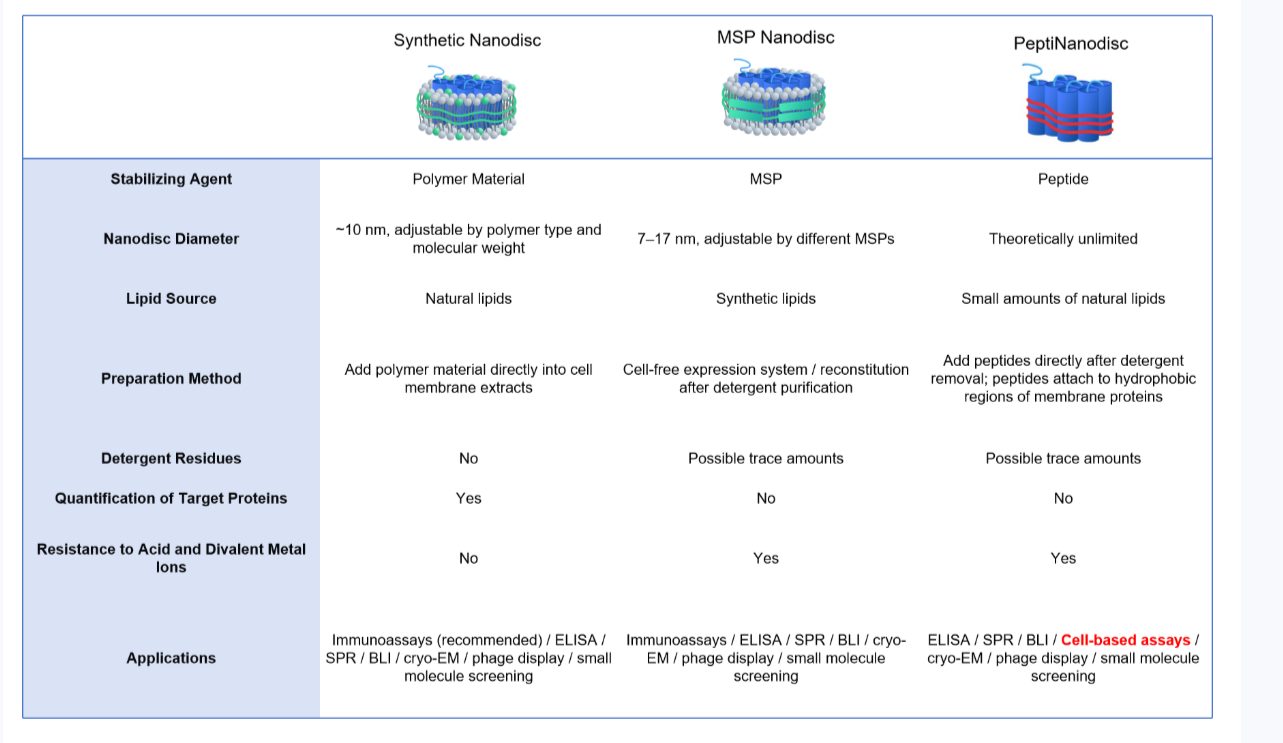
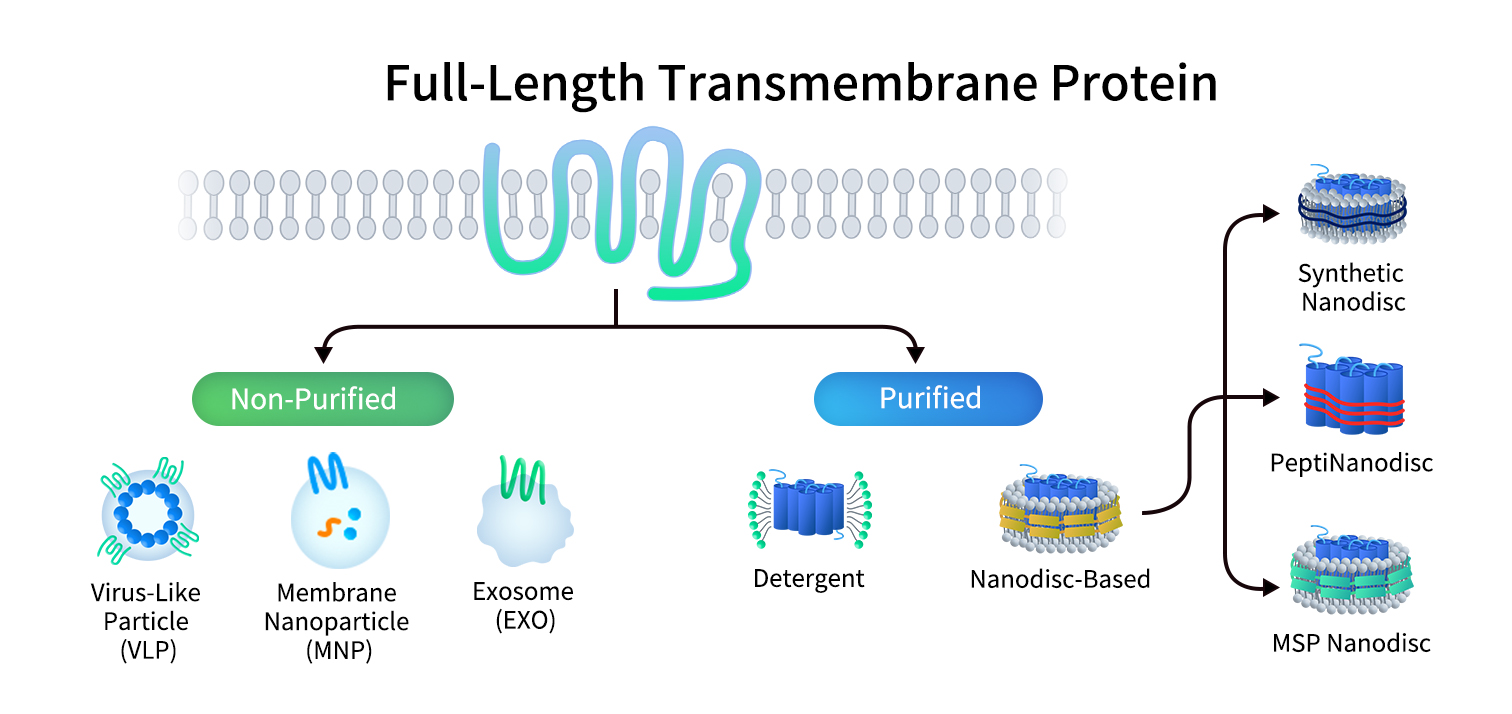
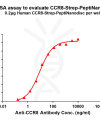
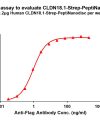
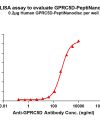
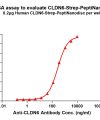
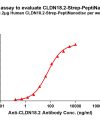
PeptiNanodisc utilizes specially designed peptides to wrap around the hydrophobic regions of membrane proteins (similar to a peptide-based disc), thereby protecting them from the aqueous environment. View more >>
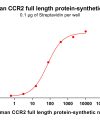
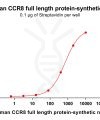
Synthetic Nanodiscs use specialized polymers to wrap around the hydrophobic regions of full-length membrane proteins. The polymers solubilize cell membranes and reorganize native phospholipids to form stable nanodisc proteins, maintaining protein structure and activity. VIew more >>
- MSP Nanodisc
MSP nanodisc uses a specific protein called Membrane Scaffold Protein (MSP) as a stabilizer to wrap artificial phospholipid components and transmembrane proteins to form a nanodisc.