In the field of cancer therapy, microtubule inhibitors are among the most classic types of cytotoxic agents. By blocking the dynamic assembly of microtubules, they directly interfere with cell division. From taxanes and vinca alkaloids to MMAE (monomethyl auristatin E), these molecules have long been indispensable weapons in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
1. Microtubule Inhibitors
Microtubules are essential components of the cytoskeleton, involved in maintaining cell shape, intracellular transport, and cell division. During mitosis, the dynamic assembly and disassembly of microtubules are particularly critical. Microtubule inhibitors (MTIs) exert their antitumor effects by disrupting this dynamic balance.
1.1 Classification
- Microtubule Stabilizers
- Examples: Paclitaxel, Docetaxel, Epothilones
- Mechanism: Promote microtubule polymerization and block depolymerization → excessive stabilization → mitotic failure
- Microtubule Destabilizers
- Examples: Vincristine, Vinblastine, Colchicine, Maytansine, Eribulin
- Mechanism: Prevent polymerization or promote depolymerization → collapse of the microtubule network → apoptosis
1.2 Clinical Applications
- Solid tumors: breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer, soft tissue sarcoma
- Hematologic malignancies: leukemia, lymphoma
- ADC payloads: toxins such as MMAE and DM1 are derivatives of MTIs
Today’s highlight—Eribulin—is a next-generation microtubule inhibitor derived from the marine natural product Halichondrin B. Unlike taxanes or vinca alkaloids, Eribulin binds to the plus end of microtubules, inhibiting polymerization without affecting depolymerization.
2. Eribulin: A Unique Microtubule Inhibitor
Eribulin is a synthetic analog of the marine natural product Halichondrin B, known as a “new-generation non-taxane microtubule inhibitor.”
① Mechanism of Action
- Unique binding mode: binds to the plus end of microtubules, inhibiting polymerization but not depolymerization
- Arrests the cell cycle at G2/M phase
- Induces apoptosis
- Remodels the tumor microenvironment (improves vascular structure, reduces hypoxic regions)
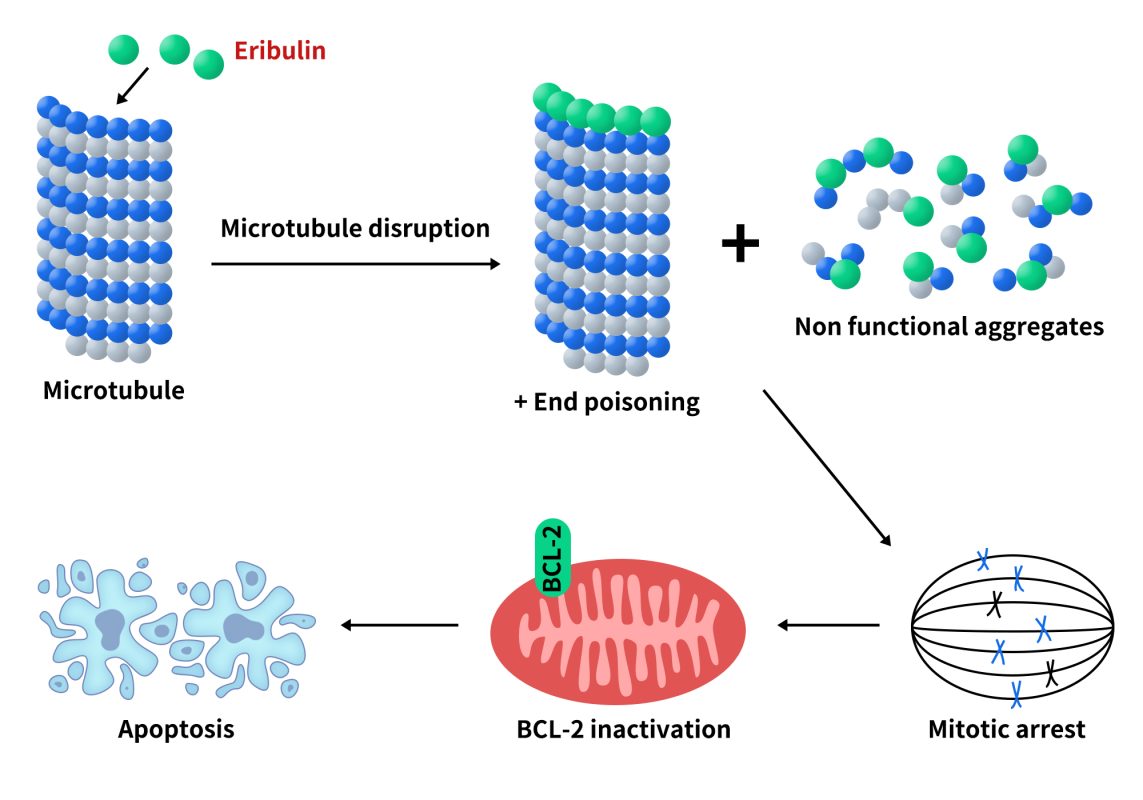
Fig 1.Working mechanism of Eribulin.
② Clinical Applications
- Metastatic breast cancer (in patients who failed prior anthracycline- and taxane-based therapies)
- Unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma (after anthracycline failure)
- Under investigation: triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) in combination with immunotherapy, soft tissue sarcoma with anti-angiogenic therapy, ovarian cancer, and more.
③ Advantages
- Distinct mechanism from traditional taxanes and vinca alkaloids → effective even in resistant patients
- Dual functions: direct cytotoxicity + modulation of the tumor microenvironment
3. A New ADC Payload Option: Eribulin IgG Labeling Reagent
Following our MMAE IgG labeling reagent, we have developed a new solution—the Eribulin IgG Labeling Reagent.
① Key Features:
- Potent payload: The microtubule inhibitory activity of Eribulin has been clinically validated.
- Convenient conjugation: Ready-to-use for IgG conjugation, simulating the ADC mechanism.
- Versatile applications: Suitable for endocytosis validation, payload screening, and antibody functional studies.
- Flexible platform: Provides researchers with a novel toxin alternative beyond MMAE.
- High stability: Accelerated stability testing demonstrates strong reagent stability (Fig. 2).
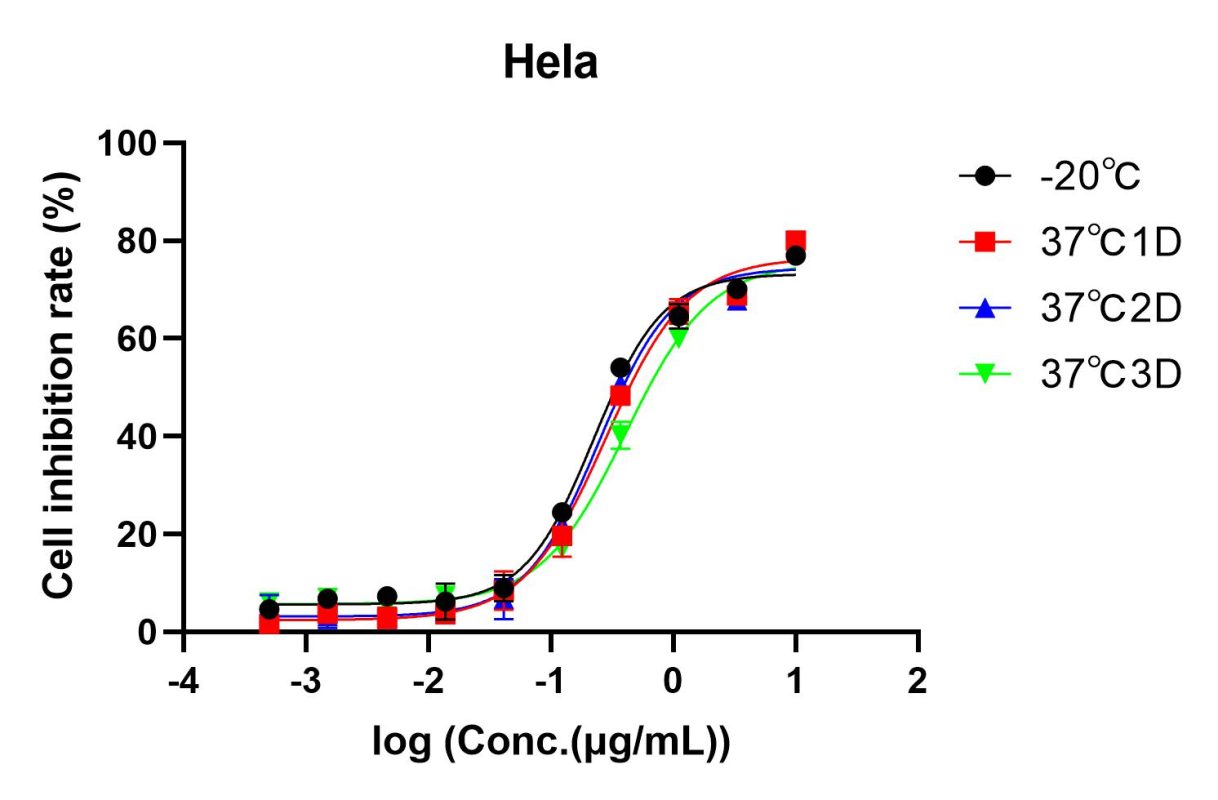
Fig 2. Accelerated stability test of AME100005. After lyophilization, the samples were stored at -20℃ (black), 37℃ for 1 day (red), 37℃ for 2 days (blue), 37℃ for 3 days (green), separately. After reconstitution, cell inhibition rate of each samples was detected by CCK8 method. The data indicate that all the samplesexhibit excellent stability.
② Application Scenarios
- Early-stage ADC validation: Evaluate antibody internalization and payload release efficiency.
- Novel payload comparison studies: Compare Eribulin with commonly used ADC payloads such as MMAE.
- Pharmacological and mechanistic exploration: Investigate the effects of microtubule-inhibiting payloads on the cell cycle and tumor microenvironment.
③ Product Data Validation
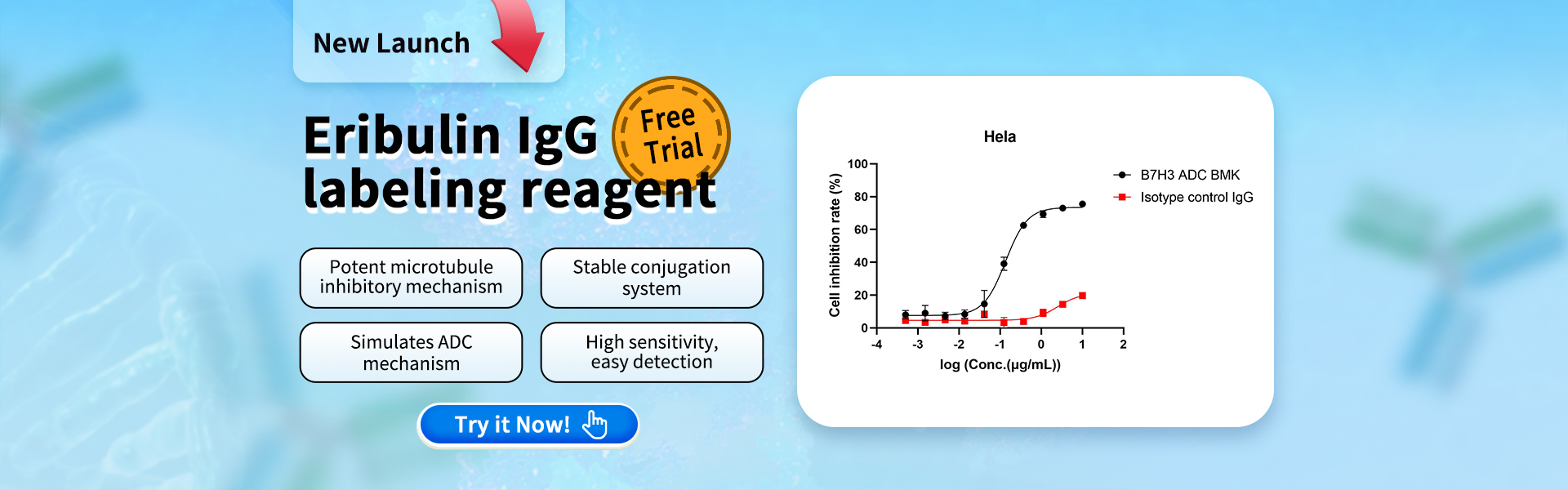
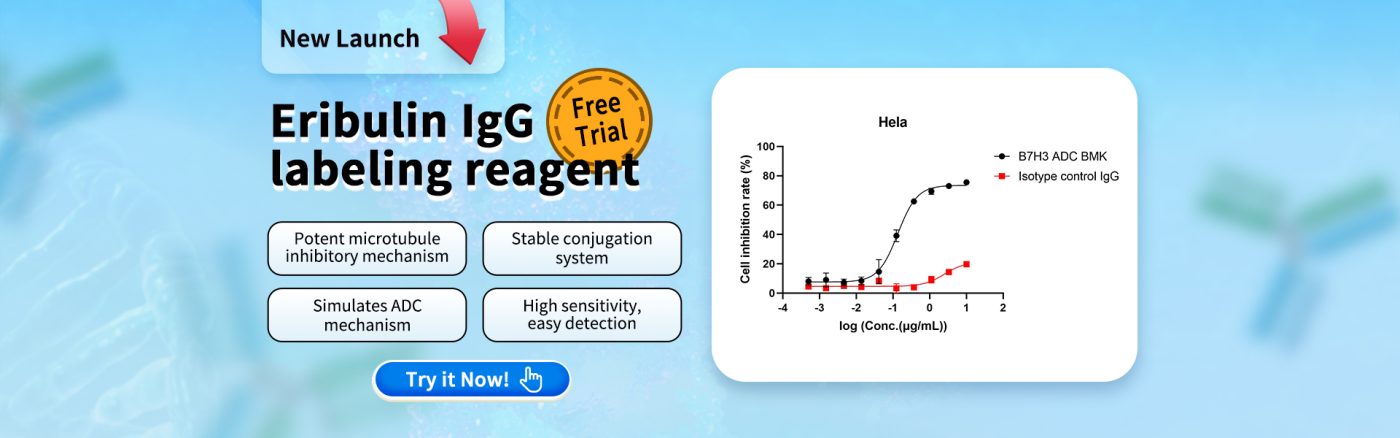
We evaluated the internalization efficiency and cytotoxicity of a B7H3 ADC (BMK) in the B7H3-high expressing Hela cell line using the Eribulin IgG Labeling Reagent (Cat. No. AME100005). The results demonstrated significant cytotoxicity of the Eribulin payload. Therefore, this reagent is highly consistent with the practical screening needs of ADC drug development!
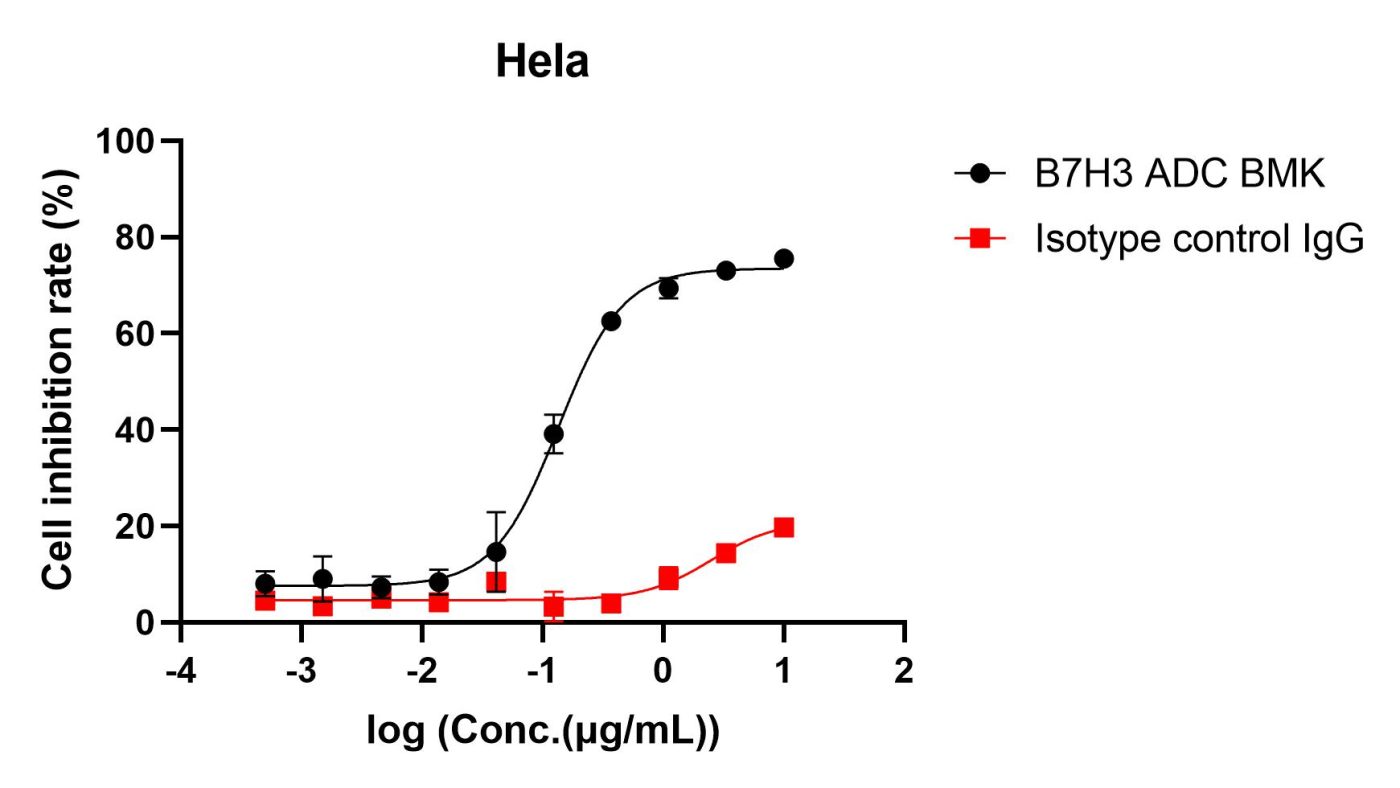
Fig 3. Cell inhibition rate of Hela detected by CCK8 method. The IC50 of B7H3 ADC BMK is 135.1ng/ml, indicating specific internalization.
From clinical anticancer therapy to research applications, Eribulin is opening new possibilities for ADC development. The DIMA Eribulin IgG Labeling Reagent enables researchers to rapidly validate antibody functions, explore novel ADC mechanisms, and take solid steps forward in drug discovery.
To thank our valued customers, DIMA is now offering a free trial promotion for the Eribulin IgG Labeling Reagent:
4. Try It Now
- Promotion period: From now until September 30, 2025
- Eligible participants: End-user customers
- Limited-time offer: Free trial! (5 μg size)
- How to participate: Contact our online customer service directly, or email us at info@dimabio.com / orders@dimabio.com
Get in touch with us today for more details—let’s work together to accelerate ADC drug development!