Recombinant IgM mAb Service
What is the structure and function of IgM
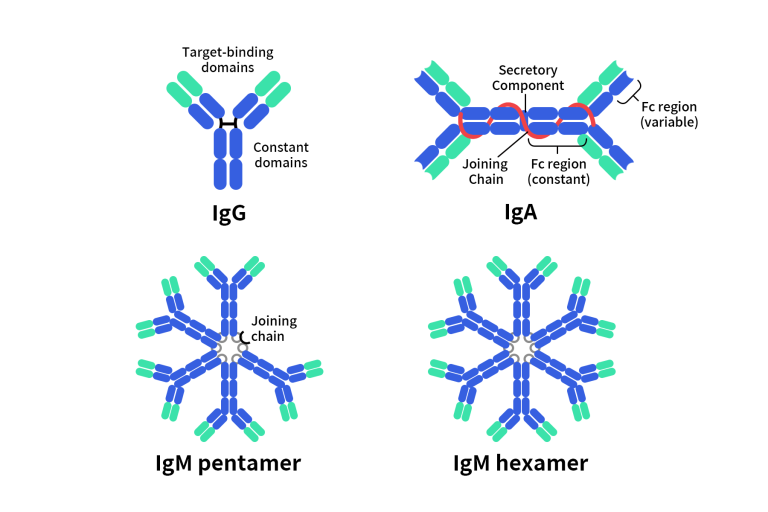
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the first antibody isotype produced during an immune response and one of the most structurally distinctive members among the five major immunoglobulin classes. Unlike IgG or IgA, IgM predominantly exists as a pentamer, with each monomer composed of two heavy and two light chains, linked together by a J chain to form a large “snowflake-like” complex. This multivalent architecture provides exceptionally strong agglutination and complement activation capabilities, enabling IgM to play a crucial role in early pathogen recognition and clearance.
With the advancement of immunotherapy and diagnostic technologies, the value of IgM is being rediscovered. Its natural high avidity and strong complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) make IgM uniquely powerful in tumor immunology, infectious disease research, and complement pathway studies. In the in vitro diagnostics (IVD) field, IgM also serves as a key biomarker for early-stage infection detection. Moreover, engineered IgM formats are increasingly used in multivalent antibody design, viral neutralization studies, and the development of targets traditionally considered “undruggable.”
However, the same polymeric nature that grants IgM its potent immune function also makes recombinant expression significantly more challenging. Its large molecular weight, complex glycosylation, and stringent folding requirements place higher demands on cell line selection, vector design, and purification workflows. As a result, producing high-quality, stable, and scalable recombinant IgM has long been considered a technical bottleneck in antibody engineering.
IgM Recombinant Expression Challenges
- Structural complexity & unstable expression
- Difficult functional validation
- Aggregation-prone & hard to purify
- Project variability; no one-size-fits-all
- High expression risk
The Advantages of DIMA BIOTECH's
- Mature mammalian expression platform
- In-house target protein library
- IgM-specific purification workflow
- Multiple customizable purification routes
- No expression = No charge
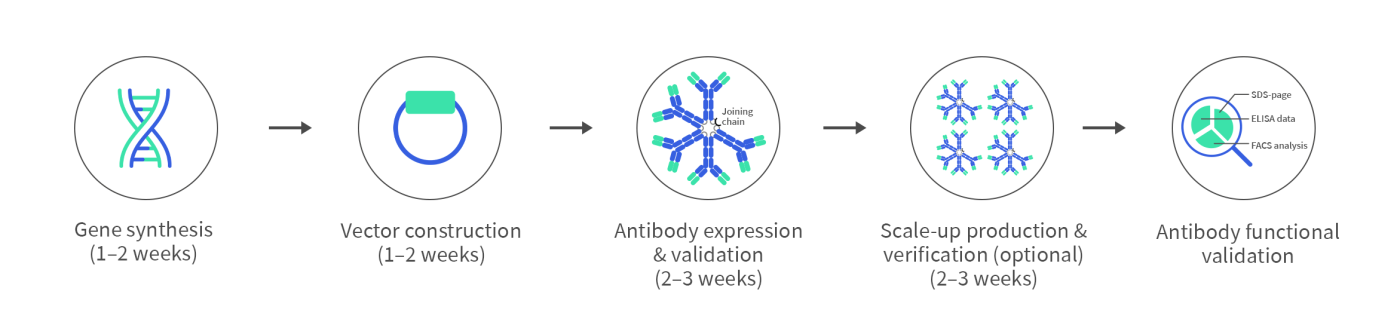
Service Content
Case Studies
Anti-TIM3 antibody(DM81) IgM mAb
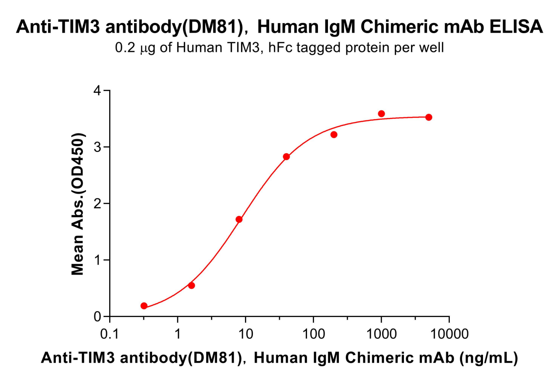
Human TIM3 Protein, hFc Tag binds Anti-TIM3 antibody IgM mAb with EC50: 8.882ng/mL
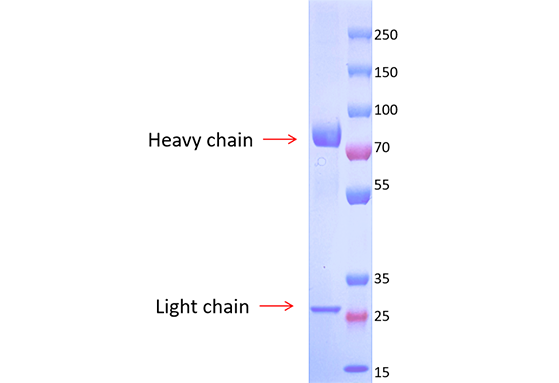
The purity of Anti-TIM3 antibody(DM81) IgM mAb determined by SDS-PAGE
FAQ
-
What makes IgM recombinant expression challenging?
IgM’s pentameric/hexameric architecture, large size, and complex glycosylation make folding and secretion difficult. Standard IgG purification workflows are generally not applicable.
-
Do you support J-chain co-expression?
Yes. We offer optional J-chain co-expression to generate structurally stable pentameric IgM when required.
-
How do you verify IgM functionality?
We can perform ELISA, FACS, or complement activation assays using in-house target proteins to confirm structural integrity and biological activity.
-
Does IgM purification cause aggregation?
We use IgM-specific purification strategies optimized to minimize aggregation, degradation, and structural disruption.
-
What deliverables do you provide?
Deliverables typically include SDS-PAGE, SEC (optional), ELISA/FACS data, concentration, purity, and multimer integrity profiles.
-
Do you charge if the expression fails?
No. We follow a zero-risk policy: No expression = No charge.
