In 2023……
On May 12th, LaNova announced that AstraZeneca will receive an exclusive global license for LM-305’s research, development, and commercialization. LM-305 is a new pre-clinical stage antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting GPRC5D. LaNova Medicines will receive an immediate payment of $55 million and $545 million in additional development and commercial milestone payments.
On May 19th, the clinical trial application for OriCAR-017 developed by OriCell Therapeutics has been accepted. This is the first CAR-T cell therapy product targeting GPRC5D in China.
In early, June of 2023, Janssen announced updated results from the pivotal Phase II study of the GPRC5D/CD3 bispecific antibody, talquetamab, in the treatment of RRMM patients, who received three or more prior lines of therapy. GlobalData estimates that it will be launched in the United States as early as 2024.
The continuous update of GPRC5D-targeted drugs has once again brought GPRC5D back to industry hotspots. Why is AstraZeneca so interested in GPRC5D drug? Which pharmaceutical companies work in this pipeline?
- What is GPRC5D?
- What are the different roles of GPRC5D and BCMA in multiple myeloma?
- What is the progress of GPRC5D-based antibody drugs for MM therapy?
- DIMA’s GPRC5D functional active proteins&antibodies
What is GPRC5D?
GPRC5D is a member of the GPRC5 receptor family, which belongs to orphan receptor class in the C family of G protein-coupled receptors. Its ligand and signal transduction mechanism has not yet been determined. GPRC5 receptor family includes four members, ie., GPRC5A, GPRC5B, GPRC5C, and GPRC5D. GPRC5A is predominately expressed in the lung [1], whereas GPRC5B can be found in multiple tissues even though it is mainly expressed in neurons [2]. The expression of GPRC5C is widespread with high levels in tissues such as kidney, liver, and cerebellum [3]. GPRC5D is only expressed in immune-privileged hair follicle region [4] in normal tissue, but it is highly expressed on the surface of primary multiple myeloma (MM) cells [5].
Human and mouse GPRC5D proteins consist of 300 and 345 amino acids, respectively. Like other GPCR receptors, GPRC5D is a seven membrane-spanning protein with four extracellular segments, out of which the first one is the longest containing 27 amino acids. The third extracellular domain contains 23 amino acids. The second and fourth extracellular domains are short, consisting of 9 amino acids and 14 amino acids, respectively.
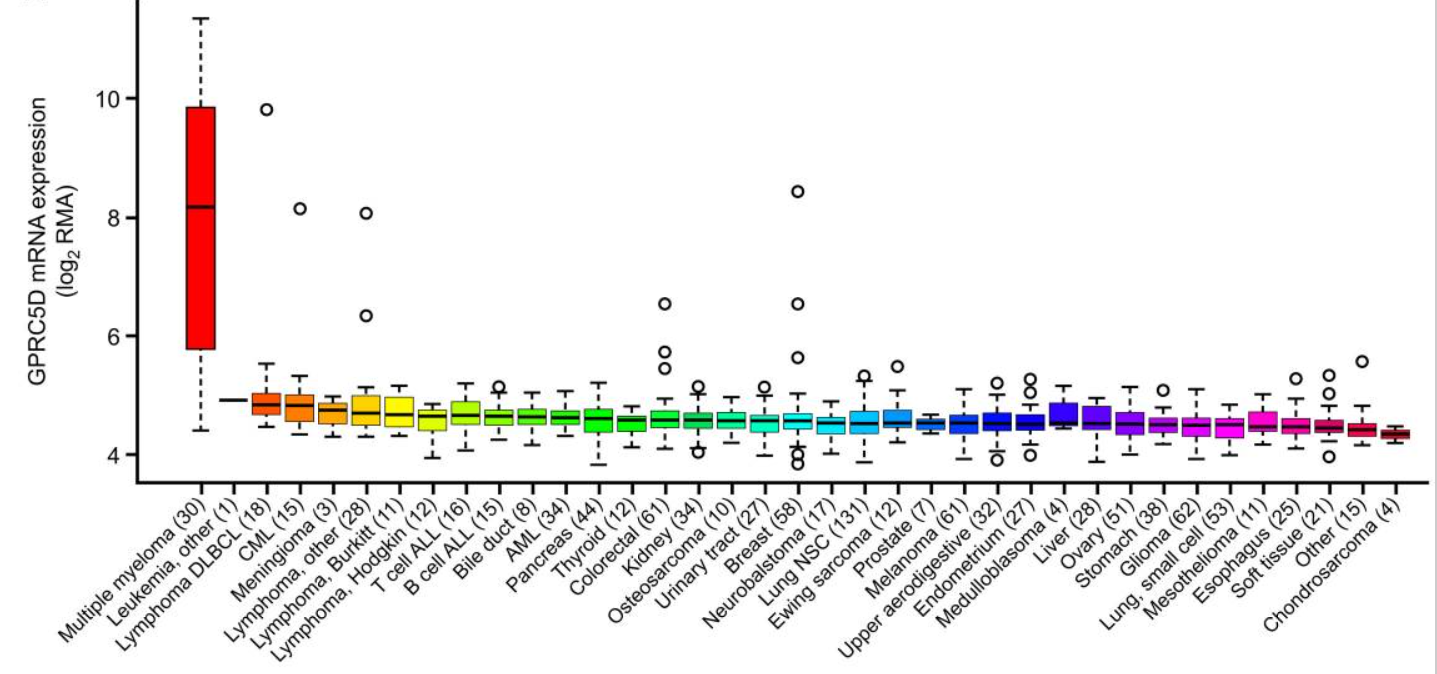
Figure 1. mRNA expression of GPRC5D in malignant cell lines
(Derived Smith EL et al., Sci Transl Med. 2019)
What is the difference between GPRC5D and BCMA in multiple myeloma?
MM is the second most common hematological cancer worldwide. Traditional approaches to treat MM include immunomodulators, proteasome inhibitors, and anti-CD38 antibodies. However, these treatments have limited effects on disease progression in MM patients, and the overall prognosis is usually poor. With the rapid development of bispecific antibody and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR-T) cell therapy, the treatment of MM has made great progress, but it is still considered incurable and almost all patients relapse after one or more treatments.
Before GPRC5D, CAR-T cell therapy targeting BCMA was the most promising method to treat MM patients. Although BCMA is expressed on most malignant plasma cells, expression is heterogeneous and may result in variable responses [6]. Moreover, cell surface BCMA expression varies over time due to γ-secretase-mediated shedding of the extracellular domain. For MM patients with BCMA-negative or low BCMA expression, relapse will still occur after receiving BCMA-targeted CAR T-cell therapy, and there is a problem of BCMA escape-driven relapse. Therefore, finding new specific MM targets e.g., GPRC5D or simultaneously targeting multiple antigens e.g., CD3, CD19, CD38, GPRC5D, has become a new trend in the treatment of MM patients. Unlike BCMA, GPRC5D is specifically expressed in multiple myeloma cells, and its expression will not decrease over time. Moreover, the expression of GPRC5D is independent of BCMA, and hence it can be used for single- or dual-targeting drugs for MM patients.
What is the progress of GPRC5D-targeted drugs for MM therapy?
According to incomplete statistics, there are 7 active GPRC5D targeted therapies in the clinical trial pipelines, including 5 in phase I, 1 in phase II, and 1 in phase III, most of which are based on bispecific antibody and CAR-T therapy.
Talquetamab
Talquetamab is a bispecific antibody developed by Johnson & Johnson, which targets both GPRC5D, the specific antigen for MM cells and CD3, T cell activation marker. Talquetamab is currently being evaluated in many clinical trials (Phase I, II and III), far ahead of other GPRC5D-targeted drugs.
In December 2022, Johnson & Johnson submitted a marketing application for BLA to FDA for the treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) with Talquetamab. Before that, Talquetamab obtained the priority drug qualification granted by European Medicines Agency, the orphan drug qualification and breakthrough therapy designation granted by FDA, and the breakthrough therapy granted by Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE).
In January 2023, Johnson & Johnson launched an international multi-center phase 3 clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of talquetamab (subcutaneous injection) combined with other drugs in patients with RRMM.
On March 31, 2023, Drug Administration Drug Evaluation Center of China announced that the talquetamab injection declared by Johnson & Johnson is planned to be included in the category of breakthrough therapy, targeting adult patients with RRMM who have received at least 3 previous treatments.
OriC-321 and OriCAR-017
OriC-321 and OriCAR-017 are two GPRC5D CAR-T products from OriCell Therapeutics for the treatment of MM patients. The OriCell used its proprietary CAR-T technology platform to construct a novel and unique signal activation domain, Ori, and insert it into the next-generation CAR molecule. Ori can increase the expansion efficiency of memory immune cells by two or more times, effectively breaking through the physical barriers of the extracellular matrix in tumor microenvironment (TME), significantly enhancing the anti-tumor activity and durability of CAR T-cells in vivo, and preventing recurrence.
OriC-321 was jointly developed by OriCell Therapeutics and Zhejiang University, targeting both BCMA and GPRC5D- and is currently in the preclinical proof-of-concept (POC) stage.
OriCAR-017 is another CAR-T cell therapy targeting GPRD5D developed by OriCell Therapeutics for the treatment of RRMM, currently evaluated in Phase I trial.
In June 2022, OriCell Therapeutics orally reported the data of phase I POLARIS clinical trial at ASCO annual meeting. As of April 30, 2022, all evaluable data of the study had shown 100% objective response rate (ORR) as well as 100% minimal residual disease (MRD) negative rate as measured by flow cytometry at day 28 after infusion in all participators, including those who relapsed after the BCMA CAR-T therapy. This data has been published in the Journal of Lancet Haematology In January 2023.
In October 2022, OriCAR-017 was granted Orphan Drug Designation from U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of RRMM.
MCARH109
MCARH109 is another GPRC5D CAR-T product jointly developed by Memorial Sloan Katherine Center (MSKCC) and Eureka Therapeutics. In vitro studies showed good curative effect. It also showed good activity in BCMA drug resistance model. MCARH109 is currently being evaluated in Phase I dose-expansion study where MM patients who failed multiple lines of therapy, including patients who relapsed after receiving BCMA CAR T-cell therapy were given MCARH109 at 4 dose levels.
RG6234
RG6234 (Forimtamig) is a GPRC5D T cell engagement bispecific antibody developed by Roche, which binds to GPRC5D and CD3. Roche said this bispecific antibody has “best-in-class” potential. In the early clinical trials, the ORR reached 71%, and complete remission (CR) reached 35% when RG6234 was used for the treatment of MM patients.
CAR-GPRC5D
CAR-GPRC5D is a GPRC5D CAR-T cell therapy developed by YaKe Biotech, which recently obtained promising results in phase II clinical trial jointly conducted with Xuzhou Medical University. The study used CAR-GPRC5D to successfully treat 33 patients with RRMM and achieved an excellent curative effect with an ORR of 91%. Among them, 9 patients had previously received BCMA CAR-T cell therapy and their ORR was 100% [7].
LM-305
LM-305 is a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting GPRC5D, which consists of an anti-GPRC5D monoclonal antibody, a degradable protease linker, and a cytotoxic-loaded monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE). It is the second product independently developed by LaNova based on its unique ADC platform. Recently, LaNova authorized an exclusive license of global development and commercialization rights of LM-305 to AstraZeneca.
LM-305 is the world’s first GPRC5D-ADC to enter the clinical stage. As early as July last year, FDA approved LM-305 to carry out clinical trials in the United States and plans to launch an open-label, multi-center phase I/II clinical study to evaluate its safety/tolerance in MM patients, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary antitumor activity.
DIMA’s GPRC5D functional active proteins&antibodies
DMA biotechnology is a biotech company focusing on preclinical products and services of druggable targets. We have various proprietary technology platforms, including a multi-pass transmembrane protein preparation platform, single-B mAb development platform, mammalian cell display-based antibody engineering platform, CAR T in vitro/in vivo functional analysis and verification platform, and pH-sensitive antibody/receptor internalization platform. We provide a one-stop shop to help pharmaceutical companies to skip the long process of hit discovery and lead screening/optimization so that they can have more time to focus on the biological mechanism and druggability research of drug targets, and hence expedite their journey from concept to IND filing.
As mentioned earlier, there are currently 7 clinical GPRC5D pipelines, including 4 CAR-T projects, 2 bispecific antibody projects, and 1 ADC project. Part of the application data of the GPRC5D rabbit monoclonal antibody of DIMA is as follows:
- FACS affinity evaluation between different humanized Anti-GPRC5D scFv and (G01~G09) and MARCH109(G00)
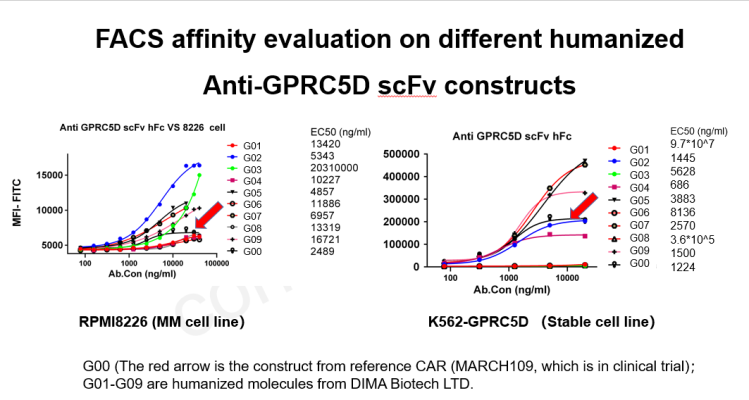
Figure 2. Affinity ranking of 9 humanized anti-GPRC5D mAbs. Compared to BMK antibody (G00) pointed by red arrow 4 out of 9 mAbs exhibit stronger binding affinity on both RPMI8226 or K562-GPRC5D stable cell line.
- In vitro tumor cell cytotoxicity assay
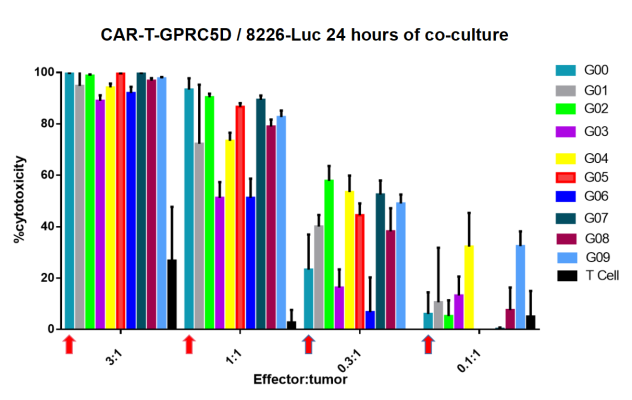
Figure 3. In vitro tumor cell cytotoxicity assay. The experimental data showed that several of CARs constructed from DIMA mAbs exhibit stronger cytotoxic capacity than bench-mark CAR (G00), pointed by red arrows, especially under low Effector:Tumor ratio.
- Animal survival data after CAR-T Therapy
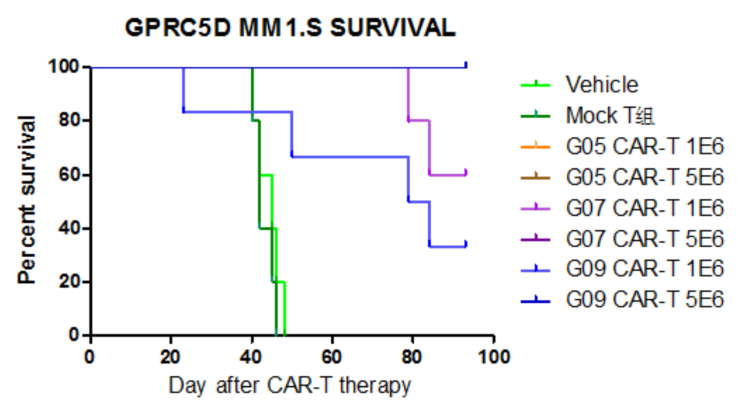
Figure 4. Animal survival data. Multiple myeloma (MM) model mice infused with two dosages of CAR T-cells exhibit elongated survival time compared with control groups.
- A RRMM patient relapsed from BCMA CAR T-cell therapy was treated with our anti-GPRC5D CAR T-cells
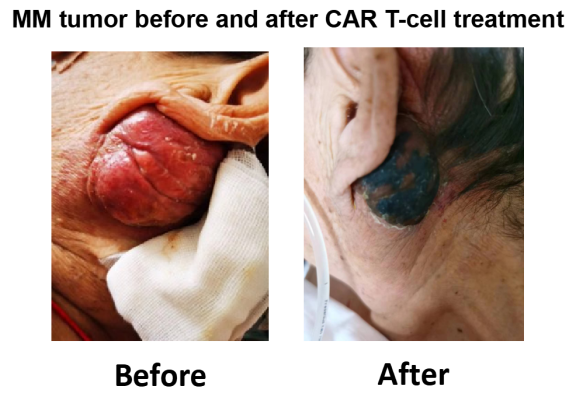
Figure 5. A RRMM patient relapsed from BCMA CAR T-cell therapy was treated with our anti-GPRC5D CAR T-cells. A metastatic tumor of large size behind patient ear nearly disappeared in 10 days after CAR T-cells infusion. (Currently, our collaborators are recruiting more patients.)
- All GPRC5D products