Cadherin-17 (CDH17) is a non-classical calcium-dependent adhesion protein predominantly expressed in the intestinal epithelium and highly upregulated in multiple gastrointestinal tumors. Due to its tumor-specific expression, CDH17 has become a promising therapeutic target. Current CDH17-targeting strategies include: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADC), Cell therapies (CAR-T/CAR-NK), Monoclonal, bispecific, or trispecific antibodies. For a comprehensive overview of CDH17 biology and ongoing clinical developments, see CDH17 Mechanisms and Drug Pipeline…
1. CDH17 Domain Selection: Why Multiple Protein Fragments Are Needed
The extracellular region of CDH17 contains seven cadherin repeats (EC1–EC7). Each domain has distinct surface exposure, conformational stability, and functional relevance, which directly impact antibody binding and assay outcomes.
EC1-EC2:Outermost domains with high accessibility;ideal for initial antibody screening.
EC3-EC5:Contribute to conformational stability;antibodies targeting these domains may show conformation-dependent binding.
EC6-EC7:Membrane-proximal domains; suitable for cell-based assay validation.
Best practice: Use multi-domain or segmented ECD proteins for primary antibody screening (ELISA, BLI, SPR), epitope mapping, domain preference analysis, and cross-comparison of antibody affinities.
Early domain-specific selection accelerates antibody discovery and reduces reliance on complex systems.
|
SKU |
Product Name |
Molecular Characterization |
|
PME100801 |
CDH17(Gln23-Met787) 6×His tag |
|
|
PME100199 |
CDH17(Ser567-Leu667) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101384 |
CDH17(Ser567-Leu667) mFc(Pro99-Lys330) |
|
|
PME101562 |
CDH17(Pro30-Gln128) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101563 |
CDH17(Ser129-Pro244) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101564 |
CDH17(Val245-Cys340) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101565 |
CDH17(Pro341-Phe449) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101566 |
CDH17(Glu450-Phe566) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101567 |
CDH17(Ala668-Gly777) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101608 |
CDH17(Gln23-Gln128) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101623 |
CDH17(Ala668-Met787) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101841 |
CDH17(Gln23-Met787) hFc(Glu99-Ala330) |
|
|
PME101842 |
CDH17(Gln23-Met787) mFc(Pro99-Lys330) |
For Domain-Specific Protein Fragments in Therapeutic Antibody Discovery…
2.CDH17 Reference Antibodies: Providing Reliable Benchmarks for Screening and Validation
In antibody development, the lack of a proper “reference” can make result interpretation difficult. For CDH17, incorporating validated reference antibodies can significantly improve screening efficiency and data reliability. These products are suitable for:
- Comparing binding capabilities of new antibodies with known antibodies
- Confirming the proper setup of experimental systems (ELISA / flow cytometry)
- Serving as positive controls in functional assays
Using a positive control helps prevent false conclusions caused by experimental system issues rather than antibody performance and enhances data comparability across batches and experiments.
|
SKU |
Product Name |
Applications |
|
BME100198 |
ELISA, Flow Cyt |
|
|
BME100198B |
ELISA, Flow Cyt |
|
|
BME100233 |
ELISA, Flow Cyt |
|
|
BME100198P |
Flow Cyt |
|
|
BME100233P |
Flow Cyt |
|
|
BME100262 |
ELISA, Flow Cyt |
3. Conformation and Functional Validation: Live-Cell Flow Cytometry
CDH17 is a typical membrane protein whose native conformation is fully maintained only in the cellular membrane environment. Antibodies screened solely with soluble proteins often require additional validation to confirm recognition of the natural membrane-bound form.
Live-cell flow cytometry is an effective method to assess whether an antibody truly binds to CDH17 in its native conformation on cell surfaces. Applications include:
- Validating antibody binding to membrane-expressed CDH17
- Functional studies, such as blocking or internalization assays
- Eliminating false-positive antibodies that bind soluble protein but fail to recognize the native membrane form
This strategy ensures that candidate antibodies are likely to retain activity in functional assays and provides a reliable foundation for CAR design and therapeutic antibody development.
|
SKU |
Product Name |
Applications |
|
DMC100637 |
WB; Flow Cyt |
|
|
DMC100637B |
WB; Flow Cyt |
|
|
CEL100009 |
Flow Cyt |
4. Cross-Species Studies: Timing for Mouse- and Monkey-Derived CDH17 Proteins
Before entering animal studies or translational research, it is critical to evaluate an antibody’s cross-species binding capability.
- Mouse-derived CDH17 proteins: Used to determine antibody suitability for mouse models
- Monkey-derived CDH17 proteins: Support safety and PK/PD studies in non-human primates
- Combined use of cross-species and human CDH17 proteins: Helps anticipate and mitigate key risks in in vivo studies
|
SKU |
Product Name |
Molecular Characterization |
|
PME-M100098 |
Mouse CDH17(Phe26-Met786) 6×His tag |
|
|
PME-C100029 |
CDH17(Lys30-Thr792) 10×His tag |
Explore the role of multi-species proteins in antibody drug development >>
5. Recommended CDH17 Product Pathway Across Research Stages
Rather than repeatedly testing a single product, selecting CDH17 product combinations tailored to each research stage can more efficiently advance projects to the next phase.
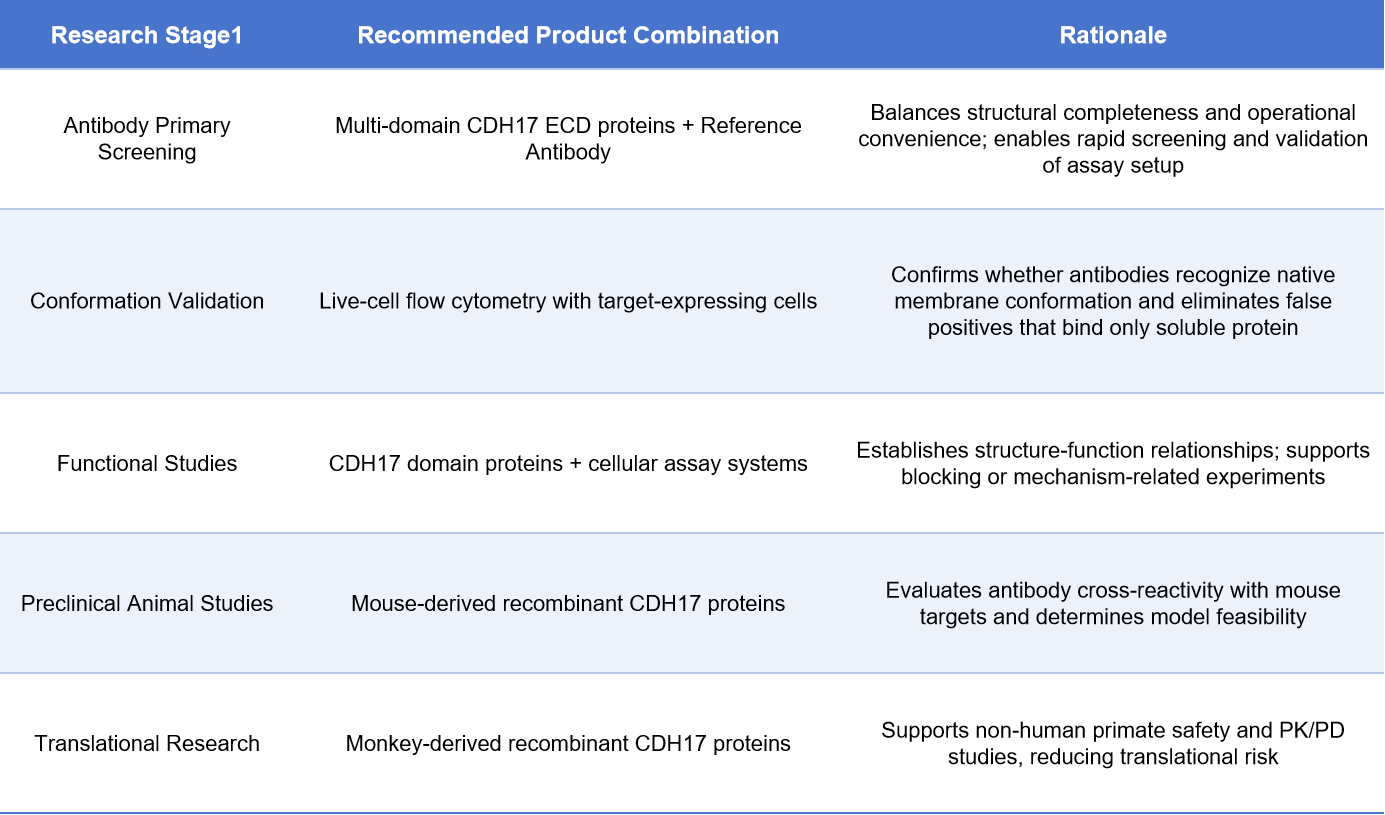
Research on CDH17 involves domain analysis, native conformation recognition, functional validation, and methodological standardization. By combining multi-domain ECD proteins, reference antibodies, and live-cell flow cytometry, researchers can systematically and efficiently perform antibody screening, epitope mapping, and functional validation.

